What is prostatitis
- Urination disorders.
- Decreased libido.
- Erectile dysfunction.
- Pain syndrome.
Classification of prostatitis
- one type—Acute prostatitis.Catalysts are infection, injury and glandular hypothermia entering the tissue. Inflammation occurs suddenly and lasts for 3-4 days. Without the necessary treatment, it can become chronic. Manifestations:
- hot,
- fever,
- Pelvic and lower back pain,
- The body is poisoned.
- Category 2—Chronic bacterial prostatitis.It starts with deterioration. Reasons for occurrence: interruption of antibiotic course, self-medication. Inflammation occurs in a latent form, with no obvious manifestations, until the immune system is severely weakened and infection causes the disease to worsen. Treatment begins with antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Category III—Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS).A disease mutated from acute inflammation of the prostate. The disorder develops slowly, causing irreversible changes that lead to tissue blockage. Congestive inflammation is divided into two subgroups:
- Category IIIa - Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome with signs of inflammation.It is characterized by distinct manifestations: low-grade fever, which in exacerbation reaches 38-38. 5°. Characteristic symptoms of male prostatitis: worsening erection, hematospermia, prolonged intercourse without orgasm, and urinary disturbance.
- Category IIIb - Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome without signs of inflammation.In this case, symptoms can only be diagnosed using instrumental research methods.
- Category 4—Asymptomatic (no symptoms) chronic prostatitis.It is considered a poorly understood disease and its etiology is not entirely clear. Some leading urologists suggest that the cause of the disease is age-related. There are no pathological symptoms.
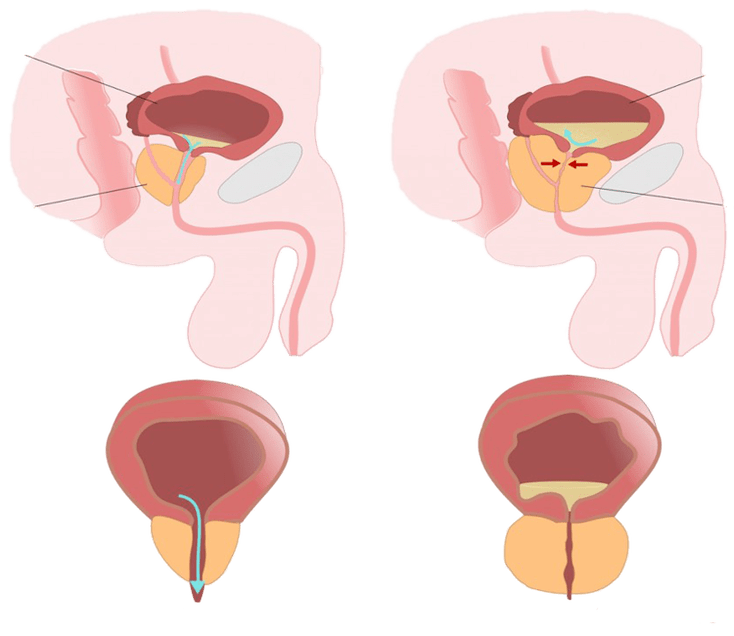
Why is prostatitis dangerous?

- erectile dysfunction-Scarring and adhesions caused by inflammation can block normal blood flow in the cavernous blood vessels. At the same time, the prostate's ability to process testosterone decreases. Decreased libido. In the acute phase, friction and ejaculation can cause pain. All of the above conditions can cause an erection to worsen. In some cases, complete impotence is diagnosed.
- infertility— Chronic inflammation affects not only the prostate but also spreads to adjacent parts and organs of the genitourinary system. Degenerative disease usually manifests itself in the ligaments: testicles + glandular tissue. Decreased quality and quantity of spermatogenesis. Pregnancy is problematic in men with advanced prostatitis.
- development of related diseases- Inflammation can spread to adjacent organs of the genitourinary system:
- urethra,
- bladder,
- kidney,
- scrotum
- die— There is a danger of death from purulent disease. If acute male prostatitis is not treated in time, suppuration occurs and develops into an abscess, the patient's life will be in danger. A ruptured cavity in the rectum can cause systemic poisoning and possibly death.
In severe cases, surgery may be required. Unlike adenomas or malignant growths, surgery is extremely rare and does not guarantee prevention of recurrence.
Which doctor treats prostatitis

- Psychiatrist— Help is needed if pain and other manifestations lead to psychological rejection of sexual relations, impotence without physical disease.
- immunologist——Long-term antimicrobial drug treatment takes a strong toll on the body. Protective functions and ability to fight infection are reduced. Some forms of prostatitis begin as an autoimmune disease. In each case, the help of an immunologist is needed.
- surgeon— Opening purulent abscesses, performing TUR, prostatectomy and removal of calcifications are all done by specialists. A surgeon's help is needed to remove adhesions in the seminiferous ducts and restore reproductive function.
How to recognize prostatitis
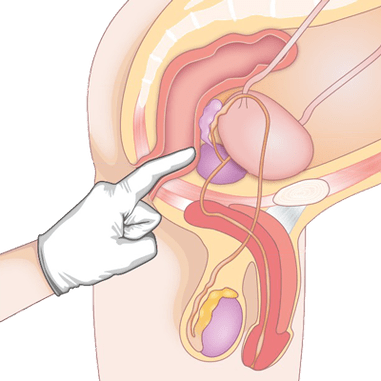
- Rectal method— The doctor probes the structure of the glands by inserting a finger into the anus, which allows any abnormalities and deviations to be identified.
- Ultrasound and transrectal ultrasonography— Diagnostic ultrasound remains the research standard due to its low cost and availability. The monitor shows loose gland structure, indicating inflammation; calcification and other signs of prostatitis can be detected.
- Clinical and biochemical tests of blood and urine- Shows the presence of inflammation and identifies the source of infection.
- Sperm diagram- Decreased sperm motility and velocity, characteristic symptoms of congestive prostatitis and obstruction of glandular tissue. During infectious diseases, bacteria and pathogens are found in semen.
- MRI and PET-CT- The most reliable diagnostic method. Because of the high cost, the test is only done when the results of a previous test are unclear and when cancer is suspected.
How long will the treatment take
Once your condition is stable and in remission, you'll need to take herbal medicines regularly, participate in physical therapy to prevent disease, and maintain your men's health in other ways.
How is prostatitis treated?
with the help of drugs
- NSAIDs- Relieves inflammation, heat and fever. They have a mild analgesic effect. When prostatitis begins, short-term treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs and vitamins is needed to maintain the normal state of the gland. These medications are available as suppositories, tablets, and injections.
- antibiotic- Designed to eliminate infectious or bacterial inflammatory factors. Treatment options for prostatitis are developed after the causative agent is identified and tested for resistance to antibiotics. The course of treatment is 7-10 days. In severe cases, treatment may be extended to two weeks.
- hormones- Recommended if regular courses of treatment do not bring any benefit and if libido is reduced due to advanced disease. The use of hormonal therapy in the early stages is contraindicated. These drugs are taken under the strict supervision of a urologist.
- Symptomatic drugs— To relieve pain, take acetylsalicylic acid tablets. Eliminate spasms with antispasmodics. For persistent severe pain, blockade with narcotics is required.
- vitaminsand medications to maintain prostate function. During remission, it is recommended to take medications to normalize metabolism, improve blood supply and juice production to glandular tissues. For this purpose, herbs are prescribed. To strengthen the immune system, it is necessary to use a complex of vitamins and minerals.
Self-medication is dangerous and can do more harm than good. You should consult a urologist before taking any of these medications.
Use physical therapy
- UHF and microwave.
- Magnet therapy.
- Mud therapy.
- Galvanized.
- Ultrasonic electrophoresis.
- Laser Treatment.
- Heat therapy.
natural treatment
- Apitherapy— Beekeeping products are used to eliminate inflammation and strengthen the immune system. Honey is a natural antibiotic. Used to treat: death, propolis, wax, pollen, poison. Massage the compress with honey to create a tincture.
- herbal collection- Urological compounds are available in pharmacies and you can prepare your own. Herbs treat urinary tract disorders, relieve inflammation and relieve pain. Some plants are good preservatives. Decoctions and teas are prepared from the collection and added when preparing preserves and tinctures.